In today's era of rapid scientific and technological advancements,humanity's quest to uncover the unknown remains relentless.Among the vast expanse of the unknown,the underground world poses a particularly intriguing and challenging frontier.To peel back this layer of mystery,scientists have developed a powerful exploration tool:Ground-Penetrating Radar(GPR).This technology,characterized by its non-destructive nature,high resolution,and real-time imaging capabilities,has become an indispensable"X-ray vision"in fields such as geological exploration,archaeological excavation,and engineering inspection.

I.The Basic Principles of Ground-Penetrating Radar
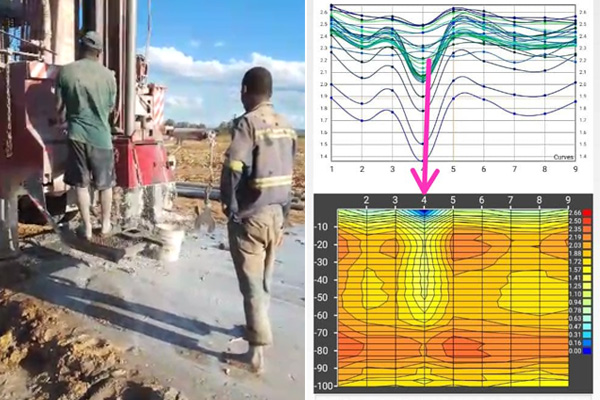
Ground-Penetrating Radar,as its name suggests,is a device that utilizes electromagnetic waves(typically high-frequency radio waves)to detect underground structures and material distributions.Its working principle is akin to bat echolocation or medical ultrasound examination but employs electromagnetic waves instead of sound waves.Specifically,GPR emits high-frequency electromagnetic wave pulses into the ground through a transmitting antenna.These pulses reflect and scatter when encountering interfaces between different media(e.g.,soil and rock,void and soil).The reflected electromagnetic waves are captured by a receiving antenna,converted into electrical signals for processing and analysis,ultimately generating images or profiles of underground structures.
II.Applications of Ground-Penetrating Radar
1.Geological Exploration:In mineral resource exploration,GPR can identify underground rock formations,faults,ore body distributions,providing crucial insights for mineral resource development.Additionally,it aids in geological disaster early warning,such as identifying potential hazardous areas for landslides and mudslides.
2.Archaeological Excavation:For ancient sites,tombs,and other cultural heritage buried underground,GPR can non-invasively detect their locations,sizes,and layouts,significantly reducing the blindness and destructiveness of archaeological excavations and preserving precious cultural heritage.
3.Engineering Inspection:In civil engineering,transportation construction,and other fields,GPR is used to detect the integrity,location,and depth of underground pipelines,cables,tunnels,and other concealed structures,as well as the stability of foundation soil layers and potential voids,ensuring engineering quality and safety.
4.Environmental Monitoring:GPR can also monitor changes in groundwater levels,soil pollution,and dynamic changes in natural environments such as glaciers and permafrost,providing scientific bases for environmental protection and disaster early warning.
III.Advantages and Challenges of Ground-Penetrating Radar
The foremost advantage of GPR lies in its non-destructive nature,high resolution,and real-time imaging capabilities,enabling the acquisition of underground information without disrupting the surface while capturing detailed underground structures.However,its application faces certain limitations,such as the rapid attenuation of electromagnetic waves in conductive media,limiting detection depth;interpretational challenges in complex geological conditions(e.g.,multilayered media,high-moisture soil);and relatively high equipment and maintenance costs.
IV.Conclusion
Ground-Penetrating Radar,a technology that integrates high-tech with practicality,is gradually transforming our understanding of the underground world.With continuous technological advancements and gradually decreasing costs,its potential for application in more fields will be further unleashed.In the future,GPR will not only continue to play a pivotal role in geological exploration,archaeological excavation,and engineering inspection but may also expand into emerging fields such as urban planning,agricultural management,and ecological monitoring.It stands as a bridge connecting the aboveground and underground worlds,contributing to humanity's exploration of nature,environmental protection,and sustainable development.