There are many factors affecting the ground water detector, and the graphs are very complicated, each graph is different, and the geological anomalies are also various. There are horizontal anomalies and vertical anomalies; there are good water anomalies and bad water anomalies; there are real anomalies and fake anomalies. As long as the work is done properly, they can be distinguished from each other.

What is considered to be doing a good job? Simply put, as long as there are geological anomalies on a ground water detector line, two different kinds of re-testing should be done, one is in-situ re-testing and the other is wrong re-testing, which have their own functions.
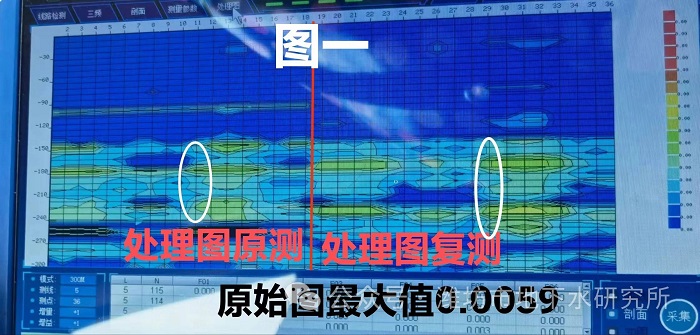
The purpose of the in-situ retest is to identify whether there is a true anomaly in the longitudinal direction. It is best to measure the ground water detector plots from the two measurements onto a single plot that can be read at a glance. Multi-channel instrument 18 measurement points are sampled at the same time, but before and after the two measurements of the map is not sampled at the same time, the middle of the interval of about seven or eight minutes, the two measurements of the map can be regarded as a "staggered remeasurement", which plays the role of, can be seen in the longitudinal direction in the black stripes or the level of the high and low value layer, whether it is true or not, and some Some false anomalies in the level caused by interference signals will not be reproduced at the same depth after the "staggered measurement". For example, in Figure 1, the horizontal high-value layers in the two ground water detector charts before and after are on the same straight line, which is a true anomaly, and there may be interlayer variable water (good water).
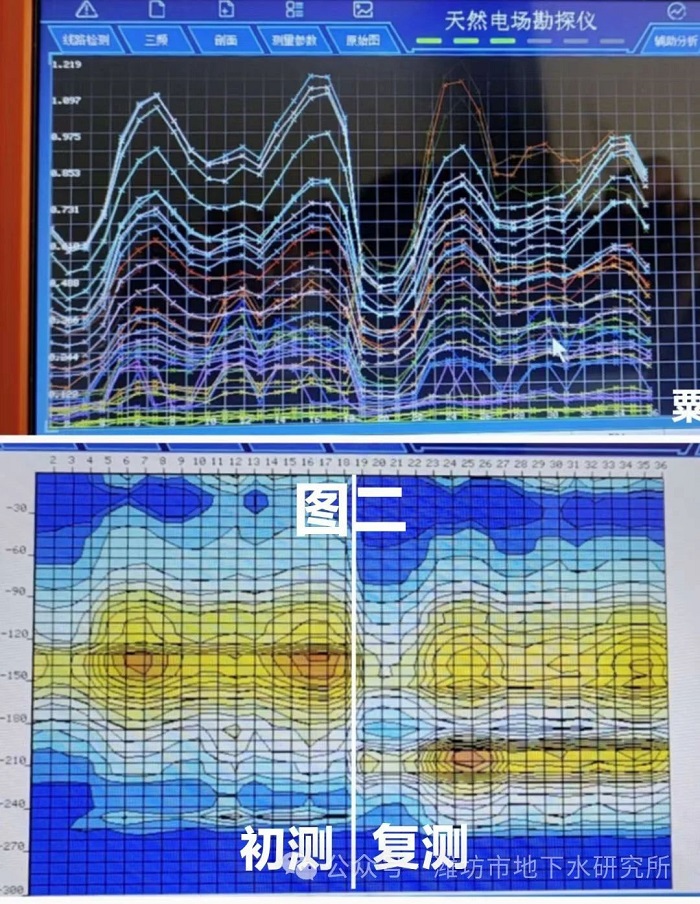
Another example is the very weak black stripes measured twice in Figure 2, which are not on the same straight line, which is a false anomaly, and there will not be interlayer water. The more in poor water areas in situ retesting inconsistency is more likely. If there are no common anomalies in both the horizontal and vertical aspects of the map, the line should be discarded. If there is a common anomaly in the horizontal direction, it is necessary to do a misalignment retest to identify its authenticity.
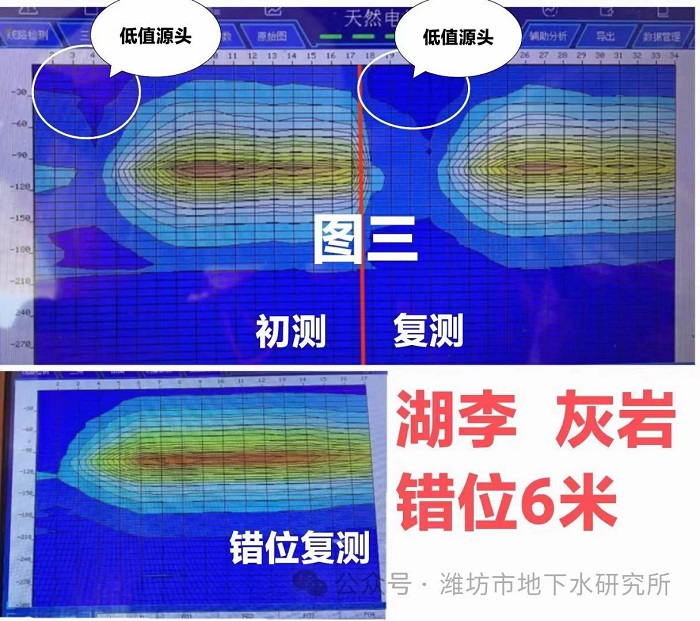
The role of the ground water detector is to identify the anomalies in the lateral anomaly is not a real anomaly, it is not because of uneven thickness of the soil layer caused by false anomalies, which can play the role of the "wrong time", but also can play the role of the "wrong position". This can not only play the role of "wrong time", but also can play the role of "wrong position". For example, Figure 3, the upper figure is the in-situ retesting, two times the measured map is very consistent, high value and low value of the contact zone are at 4 points. The lower figure is the dislocation retest map, the location has changed, the change rule of soil thickness has changed, the contact zone of high value and low value has changed from point 4 to point 2, which indicates that point 4 and point 2 are not real, they are all false anomalies, and they can't be fixed.
If there is no horizontal high-value layer or low-value layer in the longitudinal direction, i.e., there is no possibility of interlayer water change, the ground water detector in-situ retest can be not done. If there is no horizontal high-value anomaly or low-value anomaly that can be utilized, the misplaced retest can also be left out. However, this requires a lot of experience to be able to do, if you lack experience, you should still do the work at home. (Transcribed from my video number, click on my avatar to see it)








