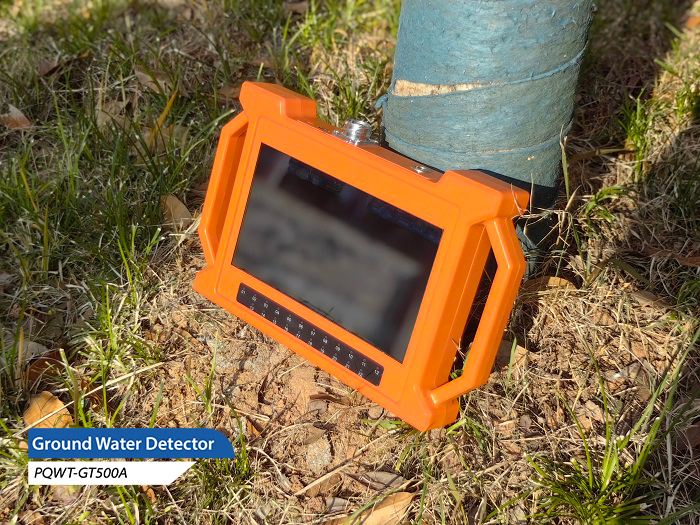
In the process of exploring groundwater resources, groundwater detectors have become an important tool in the field of geological exploration with their unique principles and technologies. Among them, the groundwater detector based on the principle of natural electric field has received widespread attention and application due to its efficient and accurate detection capability. This article will provide a detailed introduction to the principle of natural electric fields and their application in groundwater detectors.

1、 The principle of natural electric field
Natural electric field refers to the electric field formed on the surface and inside of the Earth due to uneven distribution of charges. The main reasons for its existence are:
1. Oxidation reduction reaction at the contact surface between electronic conductors and solution: When electronic conductors of different rocks and ores come into contact with groundwater solution underground, oxidation-reduction reactions occur, forming charge distribution and generating an electric field.
2. The seepage and filtration of groundwater: During the seepage and filtration process of groundwater in rocks, it will undergo electrochemical reactions with rocks, further affecting the distribution of charges.
3. Ion diffusion of mineralized solution and adsorption of rock skeleton: The diffusion of ions in underground mineralized solution at the rock interface, as well as the adsorption of ions by the rock skeleton, will also change the charge distribution and form an electric field.
The Earth's electric field not only exists between the atmosphere and the crust, but also generates different electric field responses through rocks or ores with different electrical conductivities in the crust. These electric field changes provide valuable information for geological exploration.
2、 Application of Natural Electric Field in Groundwater Detector
Based on the principle of natural electric fields, groundwater detectors infer the properties and distribution of underground rocks or ores by measuring changes in the electric field in the Earth's crust, in order to locate groundwater resources. The specific application principles and methods are as follows:
1. Frequency selective reception of electric field signals at multiple frequency points: Groundwater detector uses frequency selective technology to receive electric field signals at multiple different frequencies. Signals of different frequencies have varying detection capabilities for different depths of underground formations. For example, lower frequency signals have better detection effects on deeper formations, while higher frequency signals are more sensitive to shallower formations.
2. Weak signal detection technology: Due to the usually very weak electric field signals in the Earth's crust, the groundwater detector uses weak signal detection technology to amplify, filter, select frequency detection, and integrate the signals, and then condition them into digital signals for analysis. This processing method can effectively improve the signal-to-noise ratio of the signal, thereby obtaining more accurate geological information.
3. Multi channel and multi-mode data acquisition: In order to improve the efficiency of data acquisition, Groundwater Detector adopts multi-channel and multi-mode data acquisition technology, which can simultaneously collect electric field signals of multiple frequencies. This technology not only improves the accuracy of detection, but also greatly shortens the detection time.
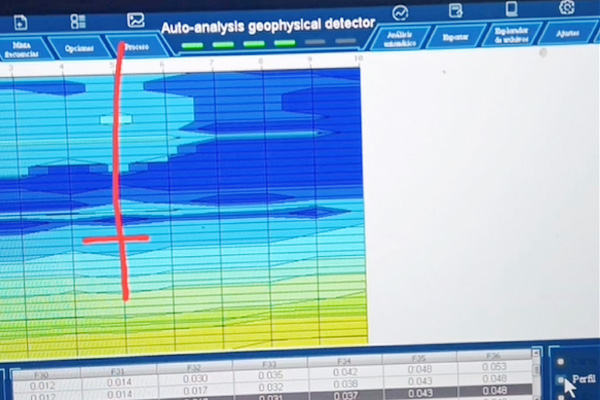
4. Automated analysis and processing: By automatically analyzing and processing the collected data, the groundwater detector can save the data in real time and draw a curve graph. This provides users with an intuitive and fast way to interpret geological information.
3、 Application Examples of Groundwater Detector
Groundwater detectors based on the principle of natural electric fields have a wide range of applications in geological exploration, hydrogeological surveys, environmental geological assessments, and other fields. Here are some specific application examples:
1. Water detection field: By observing the changes in the earth's electric field, the groundwater detector can infer the distribution, depth, and other information of underground aquifers, providing accurate positioning basis for drilling wells.
2. Geological structure research: Groundwater detectors can also help understand the distribution, thickness, lithology, and other information of geological formations, providing important data support for geological structure research.
3. Application in different terrains: This instrument is widely used in different terrains such as plains, hills, mountains, plateaus, basins, etc. It can quickly analyze changes in geological structures, determine well locations, aquifers, and aquifer depths.
4、 Conclusion
In summary, the groundwater detector based on the natural electric field principle has played an important role in the field of geological exploration with its unique detection principle and technological advantages. It not only improves the accuracy and efficiency of detection, but also provides strong technical support for the development and utilization of groundwater resources. With the continuous advancement and innovation of technology, we believe that groundwater detectors will play a more extensive and important role in the future.