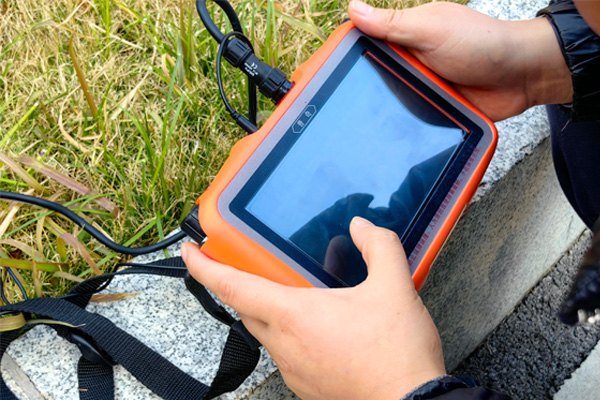
Finding groundwater sources is a crucial task in arid and water scarce areas. Ground water detector, as a modern technological product, has been widely used in his field. This article will provide a detailed introduction on how to use a ground water detector to effectively select groundwater sources.

1、 select appropriate detection points
Before using a ground water detector, it is necessary to first select a suitable detection point. Usually, areas with flat terrain or gentle slopes are easier to find water sources. When selecting detection points, they should be kept away from places such as waste, fertilizer plants, and landfills that may cause pollution to water quality. This step requires judgment based on experience or actual situations.
2、 Installation and Calibration
Follow the instructions in the user manual to correctly install, calibrate, and debug the ground water detector. This step is crucial to ensure that the instrument can function properly. Different types of ground water detectors, such as artificial ground water detectors, mechanical ground water detectors, and electronic ground water detectors, may have different installation and calibration steps.
3、 Wiring and parameter settings
1. Wiring: Before conducting measurements, straight wiring is required. Place cables and electrode rods in the area to be tested based on the selected number of measurement points. Ensure that the electrode rod and cable are in good contact, and that the electrode grounding is normal. For example, when measuring 10 measurement points, 14 electrode rods need to be placed.
2. Parameter setting: Check if the circuit is normal, long press the circuit detection light, and observe if all the circuit indicator lights below the screen are on. Next, click on "Profile" and then click on "Measurement Parameter Settings" and "Line Number Settings". The line number must be changed for each location being measured. Set the number of points and subtract 4 from the actual number of connected electrode rods to obtain the actual measurement point. Finally, set the depth and adjust it to the corresponding depth that needs to be measured.
4、 Start measuring and analyzing
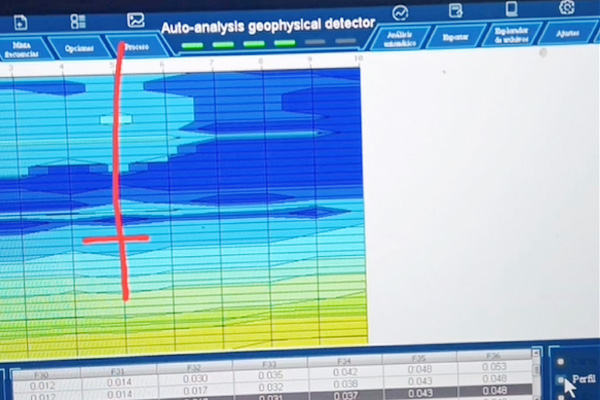
After completing the above steps, click OK, and then click Collect to start collecting data. At this point, there is a blue progress bar displayed at the bottom of the screen, and a beep sound indicating that data collection is complete. Click on the curve chart, section chart, 3D chart, and auxiliary analysis on the screen respectively to view the desired result chart and conduct on-site analysis of the measurement results according to the actual situation.
5、 Retesting and Verification
In order to verify the authenticity of the data and construct the extension and scale of anomalies, a parallel line is usually re measured 5 meters away from the original survey line. Compare the two measurement results to confirm whether the measurement results are true and whether the data collection is effective. By combining curve and profile diagrams with measurement data and geological lithology, the geological structure is comprehensively analyzed to determine the presence and conditions of water storage structures and determine the well location.
6、 Precautions
1. Before using a ground water detector for measurement, it is necessary to ensure that the equipment is well grounded to prevent damage to the equipment or injury to personnel caused by live electricity.
2. When setting parameters, it is necessary to correctly select the measurement line number and depth, otherwise it will affect the measurement results.
3. When conducting retesting, it is important to note that the distance between parallel lines should not be less than 5 meters to avoid affecting the measurement results.
4. When conducting cross-sectional measurements, it is important to ensure that the cable is well connected to the electrode rod, otherwise it will affect the measurement results.
7、 Other auxiliary methods
In addition to using ground water detectors, some traditional methods can also be combined to determine groundwater sources. For example, observing plant growth, terrain, and seasonal climate changes. In summer, areas with lower ground temperatures and prolonged exposure to sunlight generally have higher water volumes; Places that are often damp and have the slowest drainage, where groundwater is close to the ground; At the foot of the mountain, there is moisture on the ground, and in places where water vapor rises like mist in the morning, dusk, or winter, there may also be water sources.
Ground water detector is an efficient and accurate tool that can help us quickly locate groundwater sources in arid and water scarce areas. However, in order to ensure the accuracy and safety of the measurement, we need to follow the correct operating steps and precautions. Meanwhile, by combining traditional methods and experience, the success rate of finding groundwater sources can be further improved. By using ground water detectors reasonably, we can effectively solve the problem of drought and water shortage, providing reliable water sources for people's production and life.