With the continuous progress of science and technology, mankind's understanding of the internal structure of the earth is also gradually deepening. Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) as an important non-destructive testing technology, through the use of high-frequency electromagnetic waves to detect the underground environment, in geological exploration, construction, environmental protection and even military reconnaissance and other fields to show its unique advantages.
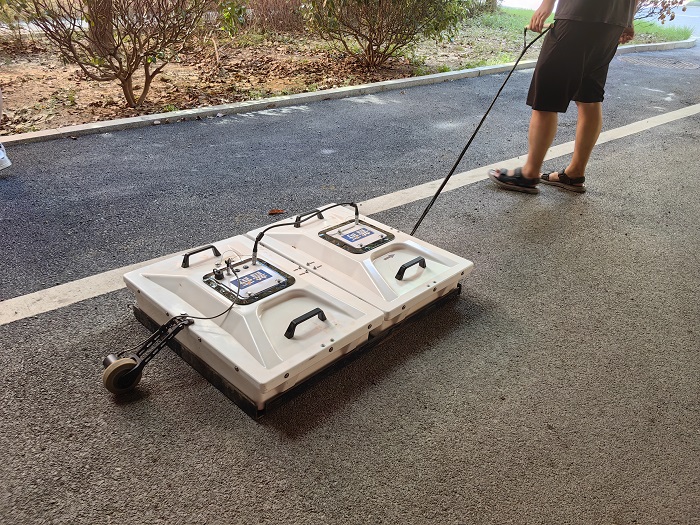

I. Working Principle
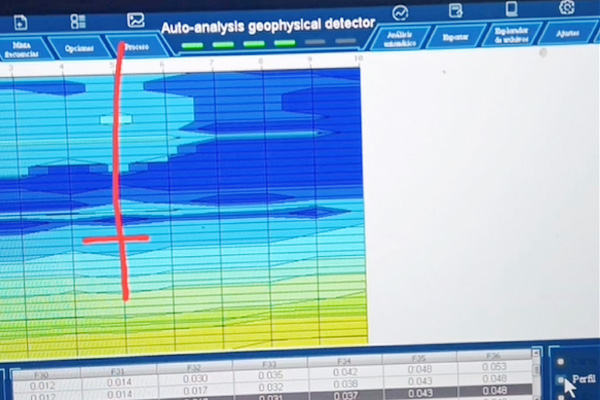
The basic working principle of ground-penetrating radar is similar to that of ordinary radar system, but it is specially designed for targets below the ground. The device mainly consists of a transmitter and a receiver. When operated, the transmitter transmits a series of short pulses of high-frequency electromagnetic waves into the ground; these electromagnetic waves will be reflected when they meet the interface of substances with different dielectric constants. Based on the reflected signal strength and its time-delay information, a two- or three-dimensional image can be constructed of the location and morphology of underground objects. Therefore, by analyzing and processing the returned signals, people will be able to “see” the various features hidden under the surface.
Second, the detection range
Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) can effectively detect many types of underground targets, and has a certain depth of penetration:
Underground structures: including but not limited to changes in soil layers, rock fault lines, artificial structures such as pipeline networks and cables.
Mineral Resource Location: Can be used to identify where potential deposits are located and how large or small they are.
Building safety assessment: checking whether the foundation of a building is stable and whether there are any problems such as cracks.
Ecological environment protection: monitoring the degree of water pollution, tracking the migration path of pollutants, etc.
Application Examples
1. Geological survey: Help scientists to discover new mineral resource sites, and can also be used in earthquake prediction studies to assess the likelihood of natural disasters occurring in a particular area.
2. Urban infrastructure management: Ensure that existing underground facilities are not accidentally damaged during road construction, improving construction efficiency while reducing safety hazards.
3. Archaeological excavation: Non-invasively revealing the layout of ancient sites and avoiding damage to artifacts caused by traditional excavation methods.
4. Public Safety Maintenance: Regularly checking the health status of bridges, discovering and repairing potential problems in a timely manner, and safeguarding the safety of passing vehicles and pedestrians.
5. National defense security: quickly and accurately determine the specific location of enemy hidden works, providing important intelligence support for the development of combat plans.
Conclusion
In summary, ground-penetrating radar plays an indispensable role in modern society with its high-resolution imaging capability and wide applicability. Whether it is in the process of scientific research or the implementation of actual engineering projects, the rational use of this technology can greatly enhance the efficiency of work and reduce the risk of unknown factors. In the future, with the optimization of the relevant algorithms and the improvement of hardware performance, I believe that the ground-penetrating radar will play a greater role in more fields, and help mankind to more comprehensively and deeply explore this beautiful and mysterious blue planet.